environment
We have a choice 3 times a day to choose plants and move the needle toward a healthier planet.
If everyone shifted to a plant-based diet
We would reduce global land use for agriculture by 75% -
because of a reduction in land used for grazing and a smaller need for land to grow crops.
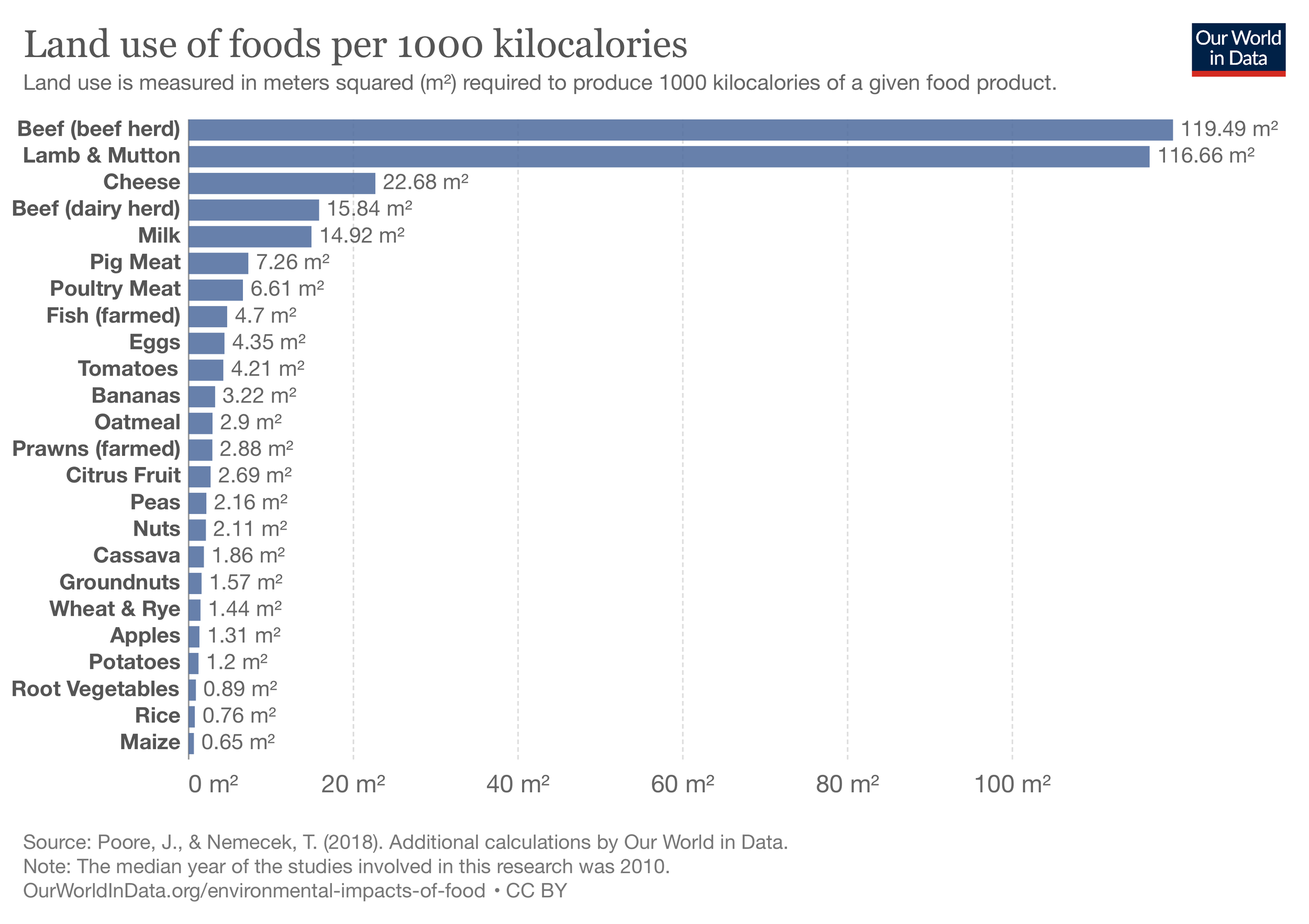
It takes almost 100 times as much land to produce a gram of protein from beef or lamb, versus peas or tofu.
H. Ritchie, 2021 Our World in Data, Oxford University
Animal agriculture is a contributor to :
for every 100 kilocalories you feed a cow, you only get 2 kilocalories of beef back. In general we see that cows are the least efficient, followed by lamb, pigs then poultry. As a rule of thumb: smaller animals are more efficient. That’s why chicken and fish tend to have a lower environmental impact. (Ritchie)
This is why eating less meat would mean eliminating large losses of calories and thereby reduce the amount of farmland we need. This would free up billions of hectares for natural vegetation, forests and ecosystems to return.
Farming practices and land use directly release at least 24% of world’s greenhouse gas emissions.
75% of land use is for animal agriculture (grazing and feed crops)
Foley, J., Ramankutty, N., Brauman, K. et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 478, 337–342 (2011).
deforestation
greenhouse gases
water use (for the animals and the feed crops)
fertilizer, pesticides and monoculture plantings for feed crops which are causing degradation of the soil
Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Economic Sector. Contribution of Working Group III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 2014.